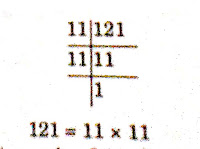NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter No. 1
Square and Cube EXERCISE 1.1

- Chapter No. 1 SQUARE AND CUBES
INTRODUCTION
1. If "n" is a number, then n × n or n2 will be known as its square and n × n × n or n3 will be called its
cube.
2. Those numbers whose unit place have numbers like 2, 3, 4, or 8 cannot be perfect square numbers.
3. If a perfect square number ends in an even number of zeroes, then they would also be perfect squares.
4. The squares and cubes of even numbers are always even numbers and squares and cubes of odd
numbers are always odd numbers.
5. The squares of any natural number "n" is the sum of the initial consecutive odd numbers.
6. If three numbers are in such a sequence that the square of the greater number is equal t the sum of the square of the remaining two numbers, then the numbers are known as Pythagoral Triplets e.g. 32 + 42 = 52 therefore (3, 4, 5) make a Pythagoral Triplet.
7. Square root is represented b the symbol " √ ". This is known as the symbol of under root or the
square root of the number. The number written under this symbol is determined.
Exercise 1.1
Q.1. Pairs the multiple factors of the following number and say whether they are perfect squares or not?
(1) 164
Sol:-
(2) 121
Sol:-
(3) 289
Sol:-
289 = 17*17
(4) 729
Sol:-
(5) 1100
Q.2. Give reasons why the given numbers are not perfect squares.
(1) 12000
Sol:- A perfect square never has odd number of zero in the end of the number, so 12000 is not a perfect square.
(2) 1227
Sol:- The units digit of a perfect square is never 2, 3, 7 or 8, so 1227 is not a perfect square.
(3) 790
Sol:- A perfect square never has odd number of zero in the end of the number, so 790 is not a perfect square.
(4) 1482
Sol:- The unit digit of a perfect square is never 2, 3, 7 or 8, so 1482 is not a perfect square.
(5) 165000
Sol:- A perfect square never has odd number of zero in the end of the number, so 165000 is not a perfect square.
(6) 15050
Sol:- A perfect square never has odd number of zero in the end of the number, so 15050 is not a perfect square.
(7) 1078
Sol:- The unit digit of a perfect square is never 2, 3, 7 or 8, so 1078 is not a perfect square.
(8) 8123
Sol:- The unit digit of a perfect square is never 2, 3, 7 or 8, so 8123 is not a perfect square.
Q.3. Find out the numbers whose squares are even numbers and whose squares are odd numbers?
Sol:- Since the square of even numbers are always even and square of odd number are always odd, so square of 14, 608, 11288, and 4010 are even numbers and square of 277, 179, 205, 1079, 1225, are odd numbers.
Q.4. Look at the given pattern and fill in the blanks:-
Sol:-

Exercise 1.2
Q.1. Identify the perfect cubes in the given numbers.
(1) 125
125 is perfect cube.
Ans.
(2) 800
Sol:-


800 =
2*2*2*2*2*5*5
800 is not a perfect cube. Ans.
(3) 729
Sol:-

729 =
3*3*3*
3*3*3
729 is a perfect cube.
Ans.
(4) 2744
Sol:-

2744 =
2*2*2*
7*7*7
2744 is a perfect cube.
Ans.
(5) 22000
Sol:-

22000 =
2*2*2*2*
5*5*5*11
22000 is not a perfect cube.
Ans.
(6) 832
Sol:-

832 is not a perfect cube.
Ans.
Q.2. Find out that smallest number which when multiplied by 256 will make the product a perfect cube.
Sol:- Prime factors of 256.

256 =
2*2*2*
2*2*2*2*2
Here, we get 2 triples of prime factors 2 but to get a third triple we will have to multiply once by 2.
So, the given number should be multiplied by 2 to get a perfect cube.
Ans.
Q.3. Find out the smallest number which when multiplied by 1352 will make the product a perfect cube.
Sol:- Prime factor of 1352

Here in the factors of 1352, we get the triple of 2 but we do not get a triple of 13. So 1352 should be multiplied by 13. So that it become a perfect cube.
Ans.
Q.4. Find out that smallest number which when multiplied by 8019 will make the quotient a perfect cube.
Sol:- Prime factor of 8019

8019 =
3*3*3*
3*3*3*11
Here in the factors of 8019, we get 2 triple of 3 but do not get a triple of 11 so that it becomes a perfect cube.
Ans.
For more help visit :
https://www.learncbse.in/ncert-solutions-for-class-8-maths/
Exercise 1.3
Q.1. Find out the square root of the given numbers by prime factorization method.
(1) 361
Sol:-
 Ans.
Ans.
(2) 400
Sol:-
 Ans.
Ans.
(3) 784
Sol:-
 Ans.
Ans.
(4) 1024
Sol:-
 Ans.
Ans.
(5) 2304
Sol:-
 Ans.
Ans.
(6) 7056
Sol:-
 Ans.
Ans.
Q.2. A group of boys bought 256 mangoes and distributed it among themselves. If each boy got the number of mangoes equal to the number of boys in the group. Find out the number of boys in the group.
Sol:- Let the number of boys in each group be x then each of x boys gets x mangoes.
So total mangoes = x*x = x2
But total number of mangoes = 256
So, x2 = 256
X2 =2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2
Taking square rot of the both sides

√ x
2=√2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 (
all numbers are in square rooot)
x = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2
x = 16
Exercise 1.4
Q.1. Find out the square root of following by division method.
(1) 529
Sol:-
 23 is Ans.
23 is Ans.
(2) 1369
Sol:-
 37 is Ans.
37 is Ans.
(3) 1024
Sol:-
32 is Ans.
(4) 5776
Sol:-
 76 is Ans.
76 is Ans.
(5) 900
Sol:-
 30 is Ans.
30 is Ans.
(6) 7921
Sol:-
0 is Ans.
(7) 50625
Sol:-
225 is Ans.
(8) 363609
Sol:-
 6703 is Ans.
6703 is Ans.
Q.2. In a cinema hall the owner wants to organize the chair in this way that the number of
rows and columns of seats should be equal. If there are total 1849 seats then find out the
numbers of rows and column.
Sol:- Given that,
the total number of seats are 1849
Then, the number of columns and rows are
1849 = 43*43
hence the number of rows and columns are 43 Ans.
Q.3. The area of a square garden is 1444 square meter, so find out the length and breadth of
that garden.
Sol:- Given that,
the area of a square garden is 1444 sq.m.
then, the length and breadth of that garden will be
we know that area of square is = L× L
so the length of the garden well be
1444 = 38 × 38
Hence, the length and breadth of the garden is same 38 m. Ans.
For more help visit :
https://www.learncbse.in/ncert-solutions-for-class-8-maths/
Exercise 1.5
Q.1. Find out the squares root of following numbers.
(1). 7.29
Sol:-
Ans.
(2). 16.81
Sol:-
 Ans.
Ans.
(3). 9.3025
Sol:-
 Ans.
Q.2. Find out the squares root of following up to two places of decimal.
Ans.
Q.2. Find out the squares root of following up to two places of decimal.
(1). 0.9
Sol:-
 Ans.
Ans.
(2). 5
Sol:-
 Ans.
Ans.
(3). 7
Sol:-
 Ans.
Ans.
For more help visit :
https://www.learncbse.in/ncert-solutions-for-class-8-maths/
Exercise 1.6
Determine the cube root of following.
(1). 125
Sol:-

Ans.
(2) 343
Sol:-

Ans.
(3). 1331
Sol:-

Ans.
(5). 9261
Sol:-

Ans.
(6) 166375
Sol:-

Ans.
(7) 4913
Sol:-

Ans.
(8) 42875
Sol:-

Ans.
For more help visit :
https://www.learncbse.in/ncert-solutions-for-class-8-maths/
WE HAVE LEARNT
1. If "n" is a number, then n × n or n2 will be known as its square and n × n × n or n3 will be called its
cube.
2. Those numbers whose unit place have numbers like 2, 3, 4, or 8 cannot be perfect square numbers.
3. If a perfect square number ends in an even number of zeroes, then they would also be perfect squares.
4. The squares and cubes of even numbers are always even numbers and squares and cubes of odd
numbers are always odd numbers.
5. The squares of any natural number "n" is the sum of the initial consecutive odd numbers.
6. If three numbers are in such a sequence that the square of the greater number is equal t the sum of the square of the remaining two numbers, then the numbers are known as Pythagoral Triplets e.g. 32 + 42 = 52 therefore (3, 4, 5) make a Pythagoral Triplet.
7. Square root is represented b the symbol " √ ". This is known as the symbol of under root or the
square root of the number. The number written under this symbol is determined.